San Andreas Fault on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The San Andreas Fault is a continental
The San Andreas Fault is a continental
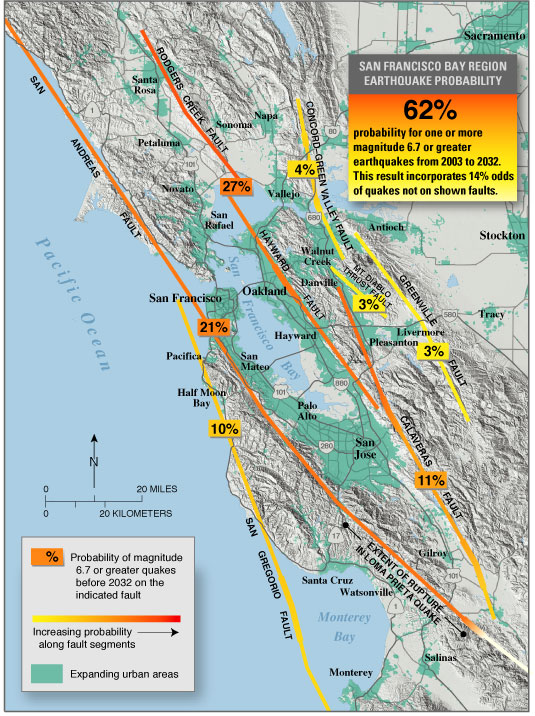 The northern segment of the fault runs from Hollister, through the
The northern segment of the fault runs from Hollister, through the

 The southern segment (also known as the Mojave segment) begins near Bombay Beach, California. Box Canyon, near the
The southern segment (also known as the Mojave segment) begins near Bombay Beach, California. Box Canyon, near the
 The San Andreas began to form in the mid
The San Andreas began to form in the mid
 A study published in 2006 in the journal ''
A study published in 2006 in the journal ''
USGS">The Parkfield, California, Earthquake Experiment United States Geological Survey, USGS
San Andreas Fault Zone Observatory at Depth
at the International Continental Scientific Drilling Program
The San Andreas Fault
by Sandra S. Schulz and Robert E. Wallace
Complete Report for San Andreas fault zone, Peninsula section (Class A) No. 1c
from the
New Scripps Study Reveals San Andreas Fault Set for the 'Big One'
at the
San Andreas Fault at Wallace Creek
– Kite Aerial Photography from the
"Scientists Search for a Pulse in Skies Above Earthquake Country"
at JPL
The Day California Cracks
at ''
Interactive Google Map
San Andreas Fault in Southern California
{{Authority control 1906 San Francisco earthquake Geography of Kern County, California Geography of Los Angeles County, California Geography of Marin County, California Geography of Monterey County, California Geography of Palmdale, California Geography of San Bernardino County, California Geography of San Francisco Geography of San Mateo County, California Geography of Santa Clara County, California Geography of Sonoma County, California Geography of the San Francisco Bay Area Geology of Imperial County, California Geology of Los Angeles County, California Geology of Riverside County, California Geology of San Bernardino County, California History of Southern California Landforms of Humboldt County, California National Natural Landmarks in California Salton Trough Seismic faults of California Strike-slip faults Active faults Supershear earthquakes San Gorgonio Pass Coachella Valley Buried rupture earthquakes
 The San Andreas Fault is a continental
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subductio ...
that extends roughly through California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
. It forms the tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents k ...
boundary between the Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
and the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific ...
, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizontal). The fault divides into three segments, each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The slip rate along the fault ranges from /yr. It was formed by a transform boundary.
The fault was identified in 1895 by Professor Andrew Lawson
Andrew Cowper Lawson (July 25, 1861 – June 16, 1952) was a Scots-Canadian geologist who became professor of geology at the University of California, Berkeley. He was the editor and co-author of the 1908 report on the 1906 San Francisco earthq ...
of UC Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of Californi ...
, who discovered the northern zone. It is often described as having been named after San Andreas Lake
San Andreas Lake is a reservoir adjacent to the San Francisco Peninsula cities of Millbrae and San Bruno in San Mateo County, California. It is situated directly on the San Andreas Fault, which is named after the valley it is in.
History
Afte ...
, a small body of water that was formed in a valley between the two plates. However, according to some of his reports from 1895 and 1908, Lawson actually named it after the surrounding San Andreas Valley. Following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
, Lawson concluded that the fault extended all the way into southern California. In 1953, geologist Thomas Dibblee
Thomas Wilson Dibblee, Jr. (11 October 1911, in Santa Barbara, California – 17 November 2004, in Santa Barbara, California) was an American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of Amer ...
concluded that hundreds of miles of lateral movement could occur along the fault.
A project called the San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth (SAFOD) near Parkfield, Monterey County
Monterey County ( ), officially the County of Monterey, is a county located on the Pacific coast in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, its population was 439,035. The county's largest city and county seat is Salinas.
Montere ...
, involved drilling through the fault during 2004–2007 to collect material and make physical and chemical observations to better understand fault behavior.
Fault zones
Northern
 The northern segment of the fault runs from Hollister, through the
The northern segment of the fault runs from Hollister, through the Santa Cruz Mountains
The Santa Cruz Mountains, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges, are a mountain range in central and Northern California, United States. They form a ridge down the San Francisco Peninsula, south of San Francisco. They separate the Pacific Ocean from ...
, epicenter of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, then up the San Francisco Peninsula
The San Francisco Peninsula is a peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area that separates San Francisco Bay from the Pacific Ocean. On its northern tip is the City and County of San Francisco. Its southern base is Mountain View, south of Palo A ...
, where it was first identified by Professor Lawson in 1895, then offshore at Daly City
Daly City () is the second most populous city in San Mateo County, California, United States, with population of 104,901 according to the 2020 census. Located in the San Francisco Bay Area, and immediately south of San Francisco (sharing its ...
near Mussel Rock
Mussel Rock is a Rock formations in the United States, rock formation on the coast of San Mateo County, California, offshore from Daly City, California, Daly City. It consists of one large and numerous smaller rocks of a type known as a Stack (ge ...
. This is the approximate location of the epicenter of the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
. The fault returns onshore at Bolinas Lagoon
Bolinas Lagoon is a tidal estuary, approximately in area, located in the West Marin region of Marin County, California, United States, adjacent to the town of Bolinas. It is a part of the Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary. In 1974, ...
just north of Stinson Beach in Marin County
Marin County is a county located in the northwestern part of the San Francisco Bay Area of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 262,231. Its county seat and largest city is San Rafael. Marin County is acros ...
. It returns underwater through the linear trough of Tomales Bay
Tomales Bay is a long, narrow inlet of the Pacific Ocean in Marin County in northern California in the United States. It is approximately long and averages nearly wide, effectively separating the Point Reyes Peninsula from the mainland of Mar ...
which separates the Point Reyes Peninsula
Point Reyes (, meaning "Point of the Kings") is a prominent cape and popular Northern California tourist destination on the Pacific coast. Located in Marin County, it is approximately west-northwest of San Francisco. The term is often applied t ...
from the mainland, runs just east of Bodega Head through Bodega Bay and back underwater, returning onshore at Fort Ross
Fort Ross ( Russian: Форт-Росс, Kashaya ''mé·ṭiʔni''), originally Fortress Ross ( pre-reformed Russian: Крѣпость Россъ, tr. ''Krepostʹ Ross''), is a former Russian establishment on the west coast of North America i ...
. (In this region around the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
several significant "sister faults" run more-or-less parallel, and each of these can create significantly destructive earthquakes.) From Fort Ross, the northern segment continues overland, forming in part a linear valley through which the Gualala River
The Gualala River is a river on the northern coast of California. Most of the river is in Sonoma County, but a portion is in Mendocino County. The headwaters of the river (measuring via its South Fork)U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography ...
flows. It goes back offshore at Point Arena
Point Arena, formerly known as Punta Arena (Spanish language, Spanish for "Sandy Point") is a small coastal city in Mendocino County, California, Mendocino County, California, United States. Point Arena is located west of Hopland, California, H ...
. After that, it runs underwater along the coast until it nears Cape Mendocino
Cape Mendocino (Spanish: ''Cabo Mendocino'', meaning "Cape of Mendoza"), which is located approximately north of San Francisco, is located on the Lost Coast entirely within Humboldt County, California, United States. At 124° 24' 34" W longitude ...
, where it begins to bend to the west, terminating at the Mendocino Triple Junction
The Mendocino Triple Junction (MTJ) is the point where the Gorda plate, the North American plate, and the Pacific plate meet, in the Pacific Ocean near Cape Mendocino in northern California. This triple junction is the location of a change in th ...
.
Central
The central segment of the San Andreas Fault runs in a northwestern direction from Parkfield to Hollister. While the southern section of the fault and the parts through Parkfield experience earthquakes, the rest of the central section of the fault exhibits a phenomenon calledaseismic creep
In geology, aseismic creep or fault creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes. Aseismic creep may also occur as "after-slip" days to years after an earthquake. Notable examples of aseismic slip in ...
, where the fault slips continuously without causing earthquakes. It was formed by a transform boundary.
Southern

 The southern segment (also known as the Mojave segment) begins near Bombay Beach, California. Box Canyon, near the
The southern segment (also known as the Mojave segment) begins near Bombay Beach, California. Box Canyon, near the Salton Sea
The Salton Sea is a shallow, landlocked, highly saline body of water in Riverside and Imperial counties at the southern end of the U.S. state of California. It lies on the San Andreas Fault within the Salton Trough that stretches to the Gulf o ...
, contains upturned strata associated with that section of the fault. The fault then runs along the southern base of the San Bernardino Mountains
The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at at San Gorgonio Mountain � ...
, crosses through the Cajon Pass
Cajon Pass (; Spanish: ''Puerto del Cajón'' or ''Paso del Cajón'') is a mountain pass between the San Bernardino Mountains to the east and the San Gabriel Mountains to the west in Southern California. Created by the movements of the San Andreas ...
and continues northwest along the northern base of the San Gabriel Mountains
The San Gabriel Mountains ( es, Sierra de San Gabriel) are a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Tr ...
. These mountains are a result of movement along the San Andreas Fault and are commonly called the Transverse Range. In Palmdale
Palmdale is a city in northern Los Angeles County in the U.S. state of California. The city lies in the Antelope Valley region of Southern California. The San Gabriel Mountains separate Palmdale from the Los Angeles Basin to the south.
On Aug ...
, a portion of the fault is easily examined at a roadcut for the Antelope Valley Freeway
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals ...
. The fault continues northwest alongside the Elizabeth Lake Road to the town of Elizabeth Lake. As it passes the towns of Gorman, Tejon Pass
The Tejon Pass , previously known as ''Portezuelo de Cortes'', ''Portezuela de Castac'', and Fort Tejon Pass is a mountain pass between the southwest end of the Tehachapi Mountains and northeastern San Emigdio Mountains, linking Southern Califor ...
and Frazier Park, the fault begins to bend northward, forming the "Big Bend". This restraining bend is thought to be where the fault locks up in Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most po ...
, with an earthquake-recurrence interval of roughly 140–160 years. Northwest of Frazier Park, the fault runs through the Carrizo Plain, a long, treeless plain where much of the fault is plainly visible. The Elkhorn Scarp defines the fault trace along much of its length within the plain.
The southern segment, which stretches from Parkfield in Monterey County
Monterey County ( ), officially the County of Monterey, is a county located on the Pacific coast in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, its population was 439,035. The county's largest city and county seat is Salinas.
Montere ...
all the way to the Salton Sea
The Salton Sea is a shallow, landlocked, highly saline body of water in Riverside and Imperial counties at the southern end of the U.S. state of California. It lies on the San Andreas Fault within the Salton Trough that stretches to the Gulf o ...
, is capable of an 8.1-magnitude earthquake. At its closest, this fault passes about to the northeast of Los Angeles. Such a large earthquake on this southern segment would kill thousands of people in Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside, and surrounding areas, and cause hundreds of billions of dollars in damage.
Plate boundaries
ThePacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
, to the west of the fault, is moving in a northwest direction while the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific ...
to the east is moving toward the southwest, but relatively southeast under the influence of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
. The rate of slippage averages about a year across California.
The southwestward motion of the North American Plate towards the Pacific is creating compressional forces along the eastern side of the fault. The effect is expressed as the Coast Ranges. The northwest movement of the Pacific Plate is also creating significant compressional forces which are especially pronounced where the North American Plate has forced the San Andreas to jog westward. This has led to the formation of the Transverse Ranges in Southern California, and to a lesser but still significant extent, the Santa Cruz Mountains
The Santa Cruz Mountains, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges, are a mountain range in central and Northern California, United States. They form a ridge down the San Francisco Peninsula, south of San Francisco. They separate the Pacific Ocean from ...
(the location of the Loma Prieta earthquake in 1989).
Studies of the relative motions of the Pacific and North American plates have shown that only about 75 percent of the motion can be accounted for in the movements of the San Andreas and its various branch faults. The rest of the motion has been found in an area east of the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
mountains called the Walker Lane
The Walker Lane is a geologic trough roughly aligned with the California/Nevada border southward to where Death Valley intersects the Garlock Fault, a major left lateral, or sinistral, strike-slip fault. The north-northwest end of the Walker L ...
or Eastern California Shear Zone. The reason for this is not clear. Several hypotheses have been offered and research is ongoing. One hypothesis – which gained interest following the Landers earthquake
The 1992 Landers earthquake occurred on Sunday, June 28 with an epicenter near the town of Landers, California, in San Bernardino County. The shock had a moment magnitude of 7.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent'').
Earthquake ...
in 1992 – suggests the plate boundary may be shifting eastward away from the San Andreas towards Walker Lane.
Assuming the plate boundary does not change as hypothesized, projected motion indicates that the landmass west of the San Andreas Fault, including Los Angeles, will eventually slide past San Francisco, then continue northwestward toward the Aleutian Trench
The Aleutian Trench (or Aleutian Trough) is an oceanic trench along a convergent plate boundary which runs along the southern coastline of Alaska and the Aleutian islands. The trench extends for from a triple junction in the west with the Ulakh ...
, over a period of perhaps twenty million years.
Formation
 The San Andreas began to form in the mid
The San Andreas began to form in the mid Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
about 30 Mya (million years ago). At this time, a spreading center
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a diver ...
between the Pacific Plate and the Farallon Plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate. It formed one of the three main plates of Panthalassa, alongside the Phoenix Plate and Izanagi Plate, which were connected by a triple junction. The Farallon Plate began subducting under the west ...
(which is now mostly subducted, with remnants including the Juan de Fuca Plate, Rivera Plate
The Rivera Plate is a small tectonic plate (a microplate) located off the west coast of Mexico, just south of the Baja California Peninsula. It is bounded on the northwest by the East Pacific Rise, on the southwest by the Rivera Transform Faul ...
, Cocos Plate
The Cocos Plate is a young oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it. The Cocos Plate was created approximately 23 million years ago when the Farallon Plate ...
, and the Nazca Plate) was beginning to reach the subduction zone off the western coast of North America. As the relative motion between the Pacific and North American Plates was different from the relative motion between the Farallon and North American Plates, the spreading ridge began to be "subducted", creating a new relative motion and a new style of deformation along the plate boundaries. These geological features are what are chiefly seen along San Andreas Fault. It also includes a possible driver for the deformation of the Basin and Range
Basin and range topography is characterized by alternating parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is a result of crustal extension due to mantle upwelling, gravitational collapse, crustal thickening, or relaxation of confining stresses. The e ...
, separation of the Baja California Peninsula, and rotation of the Transverse Range.
The main southern section of the San Andreas Fault proper has only existed for about 5 million years. The first known incarnation of the southern part of the fault was Clemens Well-Fenner- San Francisquito fault zone around 22–13 Ma. This system added the San Gabriel Fault
The San Gabriel Fault is a geological fault in Los Angeles County, California, running about southeastward from the Ridge Basin in the Sierra Pelona-San Emigdio Mountains juncture area to the western San Gabriel Mountains that forms their southw ...
as a primary focus of movement between 10–5 Ma. Currently, it is believed that the modern San Andreas will eventually transfer its motion toward a fault within the Eastern California Shear Zone
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
. This complicated evolution, especially along the southern segment, is mostly caused by either the "Big Bend" and/or a difference in the motion vector between the plates and the trend of the fault and its surrounding branches.
Study
Early years
The fault was first identified in Northern California by UC Berkeley geology professorAndrew Lawson
Andrew Cowper Lawson (July 25, 1861 – June 16, 1952) was a Scots-Canadian geologist who became professor of geology at the University of California, Berkeley. He was the editor and co-author of the 1908 report on the 1906 San Francisco earthq ...
in 1895 and named by him after the ''Laguna de San Andreas
San Andreas Lake is a reservoir adjacent to the San Francisco Peninsula cities of Millbrae and San Bruno in San Mateo County, California. It is situated directly on the San Andreas Fault, which is named after the valley it is in.
History
Af ...
'', a small lake which lies in a linear valley formed by the fault just south of San Francisco. Eleven years later, Lawson discovered that the San Andreas Fault stretched southward into southern California after reviewing the effects of the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
. Large-scale (hundreds of miles) lateral movement along the fault was first proposed in a 1953 paper by geologists Mason Hill and Thomas Dibblee
Thomas Wilson Dibblee, Jr. (11 October 1911, in Santa Barbara, California – 17 November 2004, in Santa Barbara, California) was an American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of Amer ...
. This idea, which was considered radical at the time, has since been vindicated by modern plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
.
Current research
Seismologists discovered that the San Andreas Fault near Parkfield in central California consistently produces a magnitude 6.0 earthquake approximately once every 22 years. Following recorded seismic events in 1857, 1881, 1901, 1922, 1934, and 1966, scientists predicted that another earthquake should occur in Parkfield in 1993. It eventually occurred in 2004. Due to the frequency of predictable activity, Parkfield has become one of the most important areas in the world for large earthquake research. In 2004, work began just north of Parkfield on theSan Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth
The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth (SAFOD) is a research project that began in 2002 aimed at collecting geological data about the San Andreas Fault for the purpose of predicting and analyzing future earthquakes. The site consists of a p ...
(SAFOD). The goal of SAFOD is to drill a hole nearly into the Earth's crust and into the San Andreas Fault. An array of sensors will be installed to record earthquakes that happen near this area.
The San Andreas Fault System has been the subject of a flood of studies. In particular, scientific research performed during the last 23 years has given rise to about 3,400 publications.
The next "Big One"
 A study published in 2006 in the journal ''
A study published in 2006 in the journal ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
'' by Yuri Fialko, an associate professor at the Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography
The Scripps Institution of Oceanography (sometimes referred to as SIO, Scripps Oceanography, or Scripps) in San Diego, California, US founded in 1903, is one of the oldest and largest centers for oceanography, ocean and Earth science research ...
, found that the San Andreas fault has reached a sufficient stress level for an earthquake of magnitude greater than 7.0 on the moment magnitude scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 pape ...
to occur.
This study also found that the risk of a large earthquake may be increasing more rapidly than scientists had previously believed. Moreover, the risk is currently concentrated on the southern section of the fault, i.e. the region around Los Angeles, because strong earthquakes have occurred relatively recently on the central (1857
Events January–March
* January 1 – The biggest Estonian newspaper, ''Postimees'', is established by Johann Voldemar Jannsen.
* January 7 – The partly French-owned London General Omnibus Company begins operating.
* Janua ...
) and northern ( 1906) segments of the fault, while the southern section has not seen any similar rupture for at least 300 years. According to this study, a major earthquake on that southern section of the San Andreas fault would result in major damage to the Palm Springs
Palm Springs (Cahuilla: ''Séc-he'') is a desert resort city in Riverside County, California, United States, within the Colorado Desert's Coachella Valley. The city covers approximately , making it the largest city in Riverside County by land ...
–Indio Indio may refer to:
Places
* Indio, Bovey Tracey, an historic estate in Devon, England
* Indio, California, a city in Riverside County, California, United States
People with the name
* Indio (musician), Canadian musician Gordon Peterson
* Índio ...
metropolitan area and other cities in San Bernardino
San Bernardino (; Spanish language, Spanish for Bernardino of Siena, "Saint Bernardino") is a city and county seat of San Bernardino County, California, United States. Located in the Inland Empire region of Southern California, the city had a ...
, Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
and Imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texa ...
counties in California, and Mexicali Municipality
Mexicali Municipality is a municipality (Mexico), municipality ( es, link=no, municipio) in the Mexican States of Mexico, state of Baja California. Its municipal seat ( es, link=no, cabecera municipal) is located in the city of Mexicali. As of 20 ...
in Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
. It would be strongly felt (and potentially cause significant damage) throughout much of Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most po ...
, including densely populated areas of Los Angeles County
Los Angeles County, officially the County of Los Angeles, and sometimes abbreviated as L.A. County, is the most populous county in the United States and in the U.S. state of California, with 9,861,224 residents estimated as of 2022. It is the ...
, Ventura County
Ventura County () is a county in the southern part of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 843,843. The largest city is Oxnard, and the county seat is the city of Ventura.
Ventura County comprises the Oxnar ...
, Orange County
Orange County most commonly refers to:
*Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area
Orange County may also refer to:
U.S. counties
*Orange County, Florida, containing Orlando
*Orange County, Indiana
*Orange County, New ...
, San Diego County
San Diego County (), officially the County of San Diego, is a county in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,298,634, making it California's second-most populous county and the fi ...
, Ensenada Municipality
The municipality ( es, link=no, municipio) of Ensenada is the fourth-largest municipality in Mexico with a land area of in 2020,
about the same size as Hidalgo state and larger than five Mexican states.
Located offshore, Cedros Island and G ...
and Tijuana Municipality
Tijuana Municipality is a municipality in the Mexican state of Baja California. Its municipal seat is located in the city of Tijuana. According to the 2020 census, the municipality had a population of 1,922,523. Luis Arturo González Cruz of the ...
, Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
, San Luis Rio Colorado in Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sonora), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is d ...
and Yuma, Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
. Older buildings would be especially prone to damage or collapse, as would buildings built on unconsolidated gravel or in coastal areas where water tables are high (and thus subject to soil liquefaction
Soil liquefaction occurs when a cohesionless saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other sudden change in stress condition, in ...
). Of the study, Fialko stated:
Nevertheless, in the years since that publication there has not been a substantial quake in the Los Angeles area, and two major reports issued by the U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
(USGS) have made variable predictions as to the risk of future seismic events. The ability to predict major earthquakes with sufficient precision to warrant increased precautions has remained elusive.
The U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
most recent forecast, known as UCERF3 The 2015 Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast, Version 3, or UCERF3, is the latest official earthquake rupture forecast (ERF) for the state of California, superseding UCERF2. It provides authoritative estimates of the likelihood and seve ...
(Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast 3), released in November 2013, estimated that an earthquake of magnitude 6.7 M or greater (i.e. equal to or greater than the 1994 Northridge earthquake
The 1994 Northridge earthquake was a moment 6.7 (), blind thrust earthquake that occurred on January 17, 1994, at 4:30:55 a.m. PST in the San Fernando Valley region of the City of Los Angeles.
The quake had a duration of approximately ...
) occurs about once every 6.7 years statewide. The same report also estimated there is a 7% probability that an earthquake of magnitude 8.0 or greater will occur in the next 30 years somewhere along the San Andreas Fault. A different USGS study in 2008 tried to assess the physical, social and economic consequences of a major earthquake in southern California. That study predicted that a magnitude 7.8 earthquake along the southern San Andreas Fault could cause about 1,800 deaths and $213 billion in damage.
Cascadia connection
A 2008 paper, studying past earthquakes along the Pacific coastal zone, found a correlation in time between seismic events on the northern San Andreas Fault and the southern part of theCascadia subduction zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, a ...
(which stretches from Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are o ...
to northern California). Scientists believe quakes on the Cascadia subduction zone may have triggered most of the major quakes on the northern San Andreas within the past 3,000 years. The evidence also shows the rupture direction going from north to south in each of these time-correlated events. However the 1906 San Francisco earthquake seems to have been the exception to this correlation because the plate movement was mostly from south to north and it was not preceded by a major quake in the Cascadia zone.
Earthquakes
The San Andreas Fault has had some notable earthquakes in historic times: * 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake: About were ruptured in central and southern California. Though it is known as theFort Tejon
Fort Tejon in California is a former United States Army outpost which was intermittently active from June 24, 1854, until September 11, 1864. It is located in the Grapevine Canyon (''La Cañada de las Uvas'') between the San Emigdio Mountains and ...
earthquake, the epicenter is thought to have been located far to the north, just south of Parkfield. Two deaths were reported. Its moment magnitude
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 pape ...
was 7.9.
* 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
: About were ruptured in Northern California. The epicenter was near San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
. At least 3,000 people died in the earthquake and subsequent fires. The magnitude was estimated to be 7.8.
* 1957 San Francisco earthquake: A magnitude 5.7 quake with an epicenter on the San Andreas fault in the ocean west of San Francisco and Daly City.
* 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake: About were ruptured (although the rupture did not reach the surface) near Santa Cruz, California
Santa Cruz (Spanish for "Holy Cross") is the county seat and largest city of Santa Cruz County, in Northern California. As of the 2020 census, the city population was 62,956. Situated on the northern edge of Monterey Bay, Santa Cruz is a pop ...
, causing 63 deaths and moderate damage in certain vulnerable locations in the San Francisco Bay Area. Moment magnitude
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 pape ...
was about 6.9. This quake occurred on October 17, 1989, at approximately 5:04 pm PDT.
* 2004 Parkfield earthquake: On September 28, 2004, at 10:15 a.m. PDT, a magnitude 6.0 earthquake struck the Parkfield area. It was felt across the state, including the San Francisco Bay Area.
See also
* * * * * * *References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
USGS">The Parkfield, California, Earthquake Experiment United States Geological Survey, USGS
San Andreas Fault Zone Observatory at Depth
at the International Continental Scientific Drilling Program
The San Andreas Fault
by Sandra S. Schulz and Robert E. Wallace
Complete Report for San Andreas fault zone, Peninsula section (Class A) No. 1c
from the
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, a ...
New Scripps Study Reveals San Andreas Fault Set for the 'Big One'
at the
Scripps Institution of Oceanography
The Scripps Institution of Oceanography (sometimes referred to as SIO, Scripps Oceanography, or Scripps) in San Diego, California, US founded in 1903, is one of the oldest and largest centers for oceanography, ocean and Earth science research ...
San Andreas Fault at Wallace Creek
– Kite Aerial Photography from the
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, a ...
"Scientists Search for a Pulse in Skies Above Earthquake Country"
at JPL
The Day California Cracks
at ''
Bloomberg Businessweek
''Bloomberg Businessweek'', previously known as ''BusinessWeek'', is an American weekly business magazine published fifty times a year. Since 2009, the magazine is owned by New York City-based Bloomberg L.P. The magazine debuted in New York City ...
''
Interactive Google Map
San Andreas Fault in Southern California
{{Authority control 1906 San Francisco earthquake Geography of Kern County, California Geography of Los Angeles County, California Geography of Marin County, California Geography of Monterey County, California Geography of Palmdale, California Geography of San Bernardino County, California Geography of San Francisco Geography of San Mateo County, California Geography of Santa Clara County, California Geography of Sonoma County, California Geography of the San Francisco Bay Area Geology of Imperial County, California Geology of Los Angeles County, California Geology of Riverside County, California Geology of San Bernardino County, California History of Southern California Landforms of Humboldt County, California National Natural Landmarks in California Salton Trough Seismic faults of California Strike-slip faults Active faults Supershear earthquakes San Gorgonio Pass Coachella Valley Buried rupture earthquakes